On this page
Introduction to the DOM
August 12, 2024
On this page
What is the DOM?
A programming API for documents. The Document Object Model (DOM) is a cross-platform and language-independent interface that treats an XML or HTML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document. The DOM represents a document with a logical tree. Each branch of the tree ends in a node, and each node contains objects. DOM methods allow programmatic access to the tree; with them one can change the structure, style or content of a document. Nodes can have event handlers attached to them. Once an event is triggered, the event handlers get executed.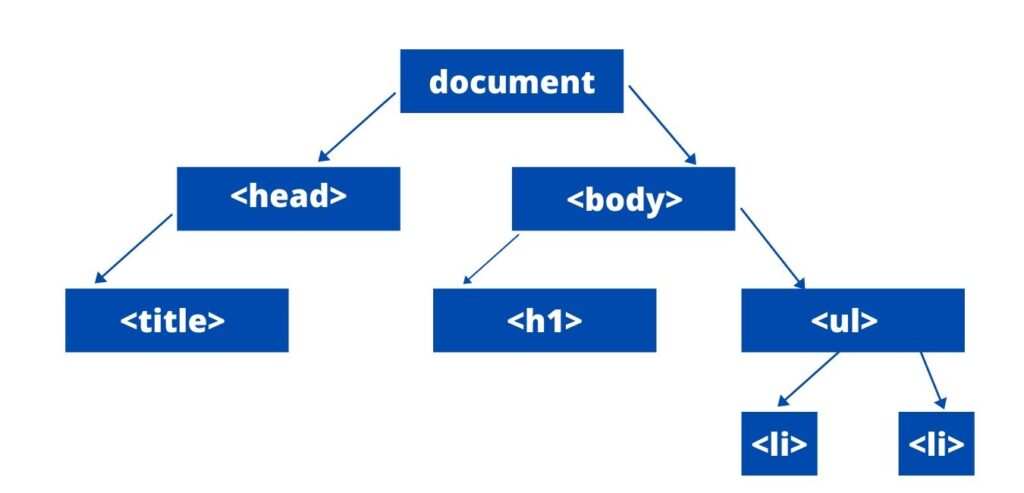
> document > console.dir(document);
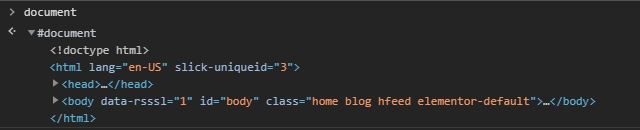
What can we do with the DOM?
1. Get an element in Javascript
> getElementByID() > getElementsByClassName() > getElementsByTagName() > querySelector() > querySelectorAll()
Example:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>The DOM Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="heading">Get an element in Javascript</h1>
<ul class="list">
<li>You can see how pages are made</li>
<li>You can manipulate it</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
> document.getElementById("heading");
< <h1 id="heading">Get an element in Javascript</h1>
2. Create things in the documents:
> createElement() > createAttribute()
Example:
var para = document.createElement('p');
para.innerHTML="This is paragraph element created from javascript";
document.body.appendChild(para);
var attr = document.createAttribute("class");
attr.value="class-para";
para.setAttributeNode(attr);
Problem:
How would you implement getElementsByAttribute?getElementsByAttribute('data-js-name', 'foo')
<div data-js-name="foo">
Suggested Steps
> Get all of the elements in the DOM > Check if they have a particular attribute > Check that the attribute has the correct value
The easy way:
function getElementsByAttribute(att, val){
return document.querySelectorAll('[' + att + '=' + ']');
}
Solution: Find a DOM node
function getElementsByAttribute(attribute, value){
var all=document.getElementsByTagName('*');
var found = [];
for(var i=0; i<all.length; i++){
element = all[i];
if(all[i].getAttribute(attribute)==value){
found.push(all[i]);
}
}
return found;
}
getElementsByAttribute('class', 'blog_title');
Events and Callbacks
Events: Occurrences that happen in the browserCommon Events: > click: the users clicks > resize: the user resize the document > mouseover: a mouse is moved over an element > load: a resource has finished loading > keydownn | keypress | keyup: the user interacts with the keyboardExample: Callbacks
window.addEventListener('load', function(event){
console.log("All resources finished loading!");
});
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Events and Callbacks are sick</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="header">Events and callbacks are SO fun.</h1>
<button id="one">Button 1</button>
<button id="two">Button 2</button>
<script type="text/javascript" src="handlers.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
document.getElementById('one').addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log('you clicked the button!');
});
document.getElementById('two').addEventListener('mouseover', function() {
document.getElementById('two').innerText = 'you hovered over me!';
});
document.body.addEventListener('timeEvent', stateTime);
function stateTime(e) {
alert("event time is: " + e.detail);
}
var myEvent = new CustomEvent('timeEvent', {
'detail': new Date()
});




