Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of other living beings, primarily of humans. It is a field of study in computer science that develops and studies intelligent machines. Such machines may be called AIs.
AI is the backbone of innovation in modern computing, unlocking value for individuals and businesses. The year 2022 brought AI into the mainstream through widespread familiarity with applications of Generative Pre-Training Transformers. The most popular applications are OpenAI’s DALL-E text-to-image tool and ChatGPT.
Types of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence can be organized in several ways, depending on stages of development or actions being performed:
- Reactive machines: IBM’s Deep Blue which beat chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997 was an example of a reactive machine.
- Limited memory: Most modern AI is considered to be limited memory. It can use memory to improve over time by being trained with new data, typically through an artificial neural network or other training model.
- Theory of mind: Theory of mind AI does not currently exist, but research is ongoing into its possibilities. It describes AI that can emulate the human mind and has decision-making capabilities equal to that of a human, including recognizing and remembering emotions and reacting in social situations as a human would.
- Self-aware: A step above theory of mind AI, self-aware AI describes a mythical machine that is aware of its own existence and has the intellectual and emotional capabilities of a human. Like theory of mind AI, self-aware AI does not currently exist.
Training Models
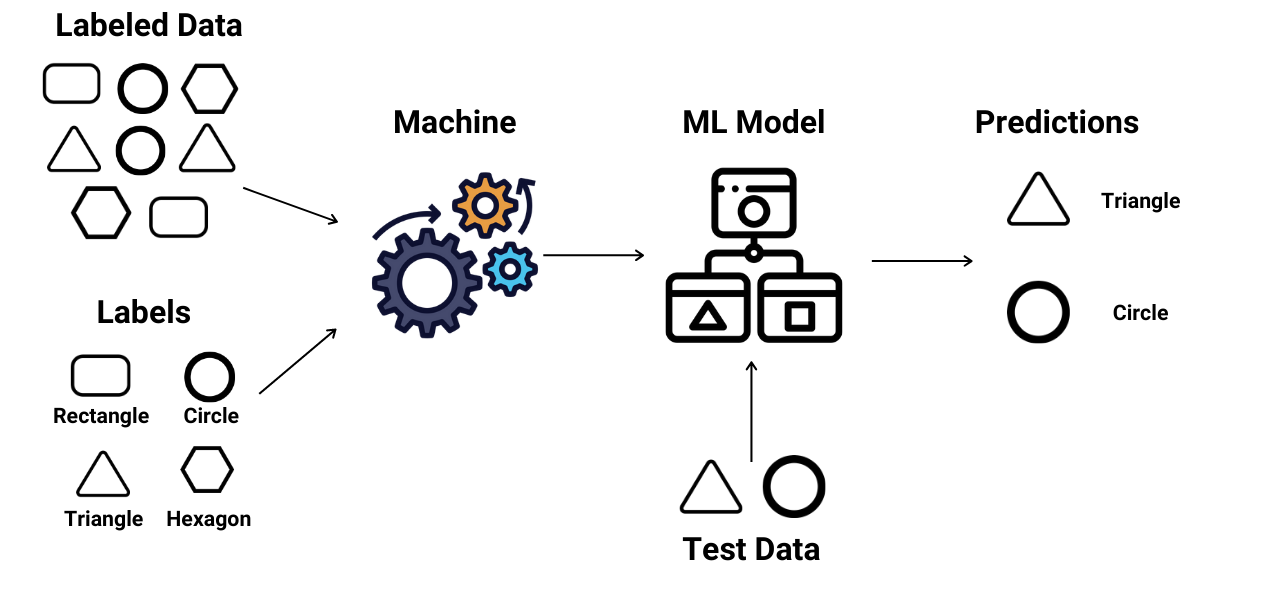
- Supervised learning: Supervised learning, also known as supervised machine learning, is a subcategory of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It is defined by its use of labeled datasets to train algorithms that to classify data or predict outcomes accurately. As input data is fed into the model, it adjusts its weights until the model has been fitted appropriately, which occurs as part of the cross-validation process. Supervised learning helps organizations solve for a variety of real-world problems at scale, such as classifying spam in a separate folder from your inbox.
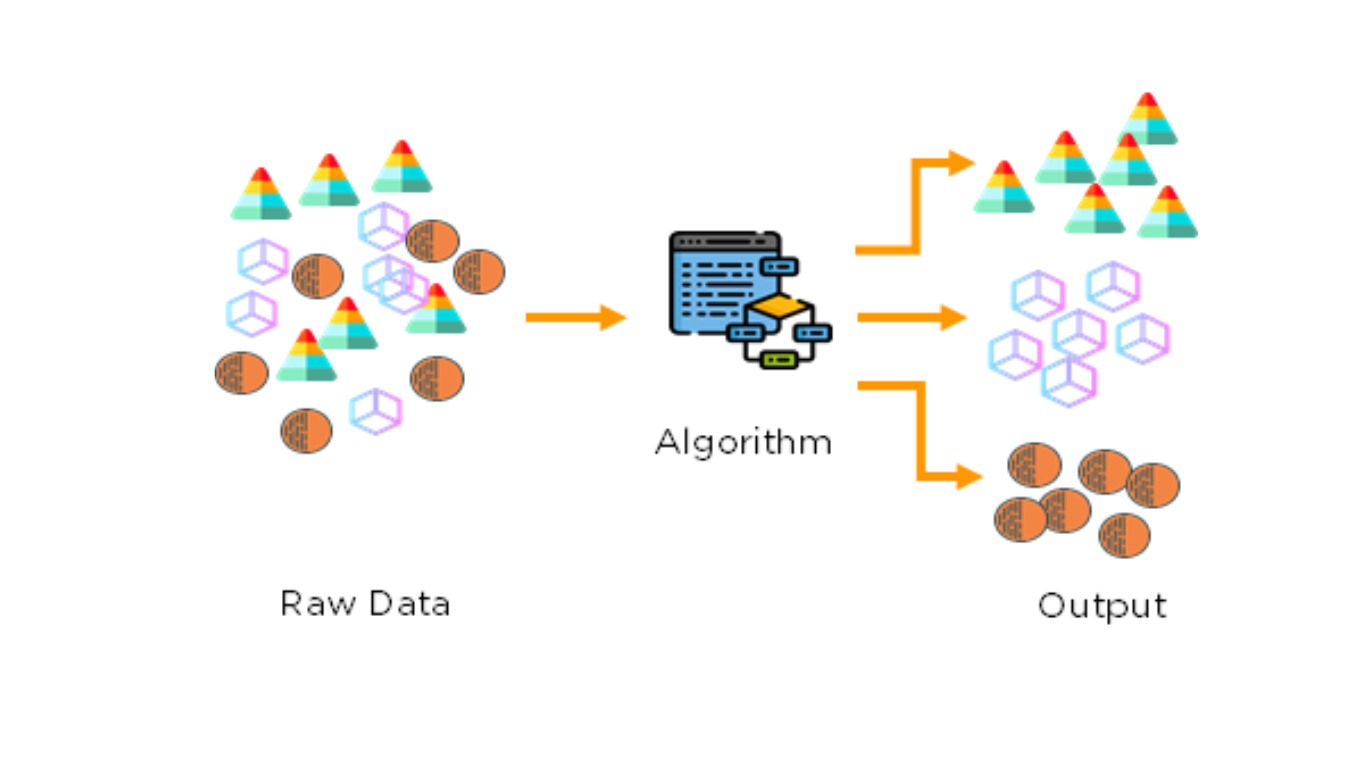
2. Unsupervised learning: Unsupervised learning, also known as unsupervised machine learning, uses machine learning algorithms to analyze and cluster unlabeled datasets. These algorithms discover hidden patterns or data groupings without the need for human intervention. Unsupervised learning models are utilized for three main tasks—clustering, association, and dimensionality reduction.
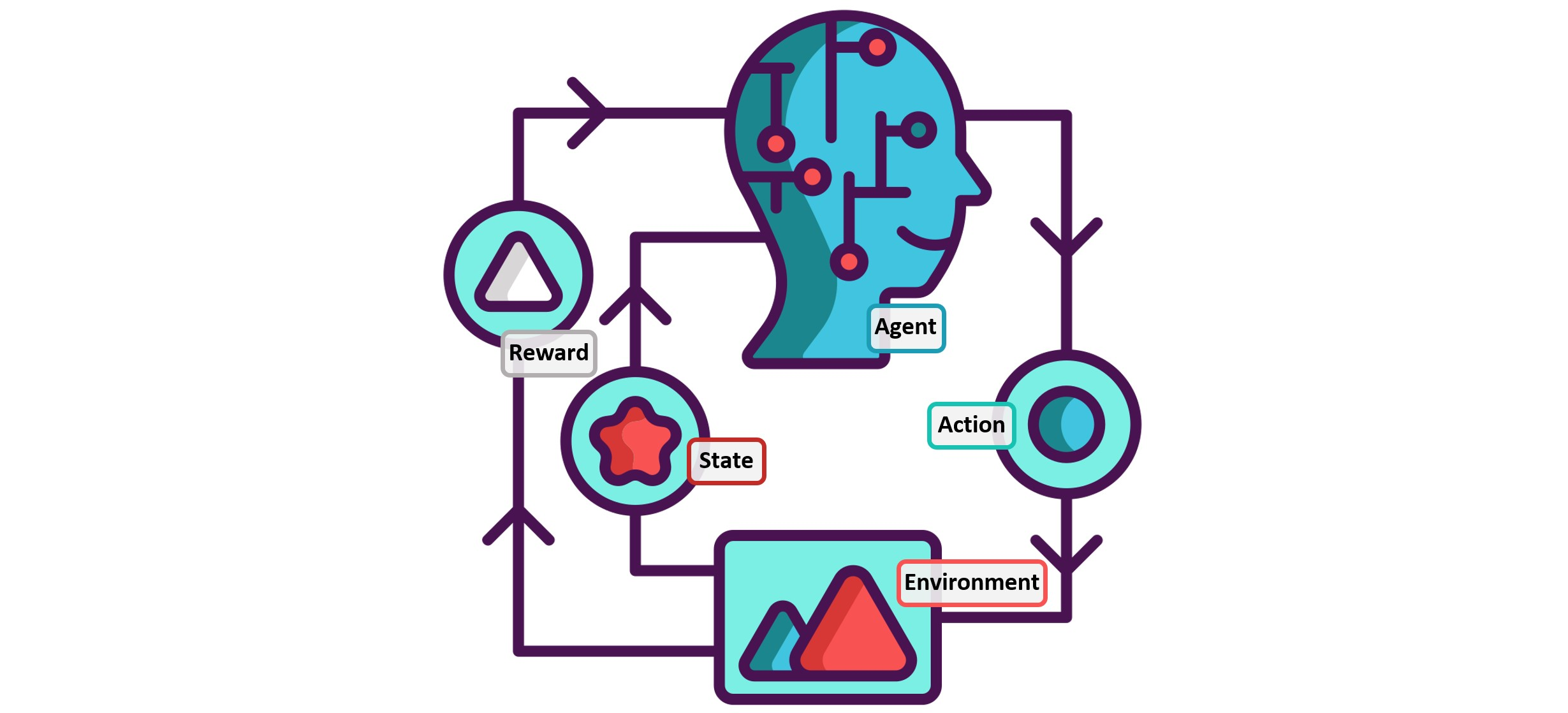
3. Reinforcement learning: Reinforcement learning is one of several approaches developers use to train machine learning systems. What makes this approach important is that it empowers an agent, whether it’s a feature in a video game or a robot in an industrial setting, to learn to navigate the complexities of the environment it was created for. Over time, through a feedback system that typically includes rewards and punishments, the agent learns from its environment and optimizes its behaviors.
Benefits of AI
- Eliminate repetitive tasks
- Fast and accurate
- Infinite availability
- Accelerated research and development
- Reduce human error
- Automation
Applications and use cases for artificial intelligence
- Image recognition
- Translation
- Speech recognition
- Predictive modeling
- Data Analytics
- Cybersecurity




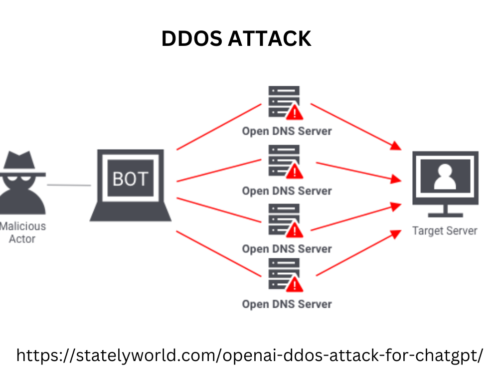














Nice information given. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you for your kind words! I’m glad you found the information helpful. Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or if there’s anything else you’d like to know. Happy reading!