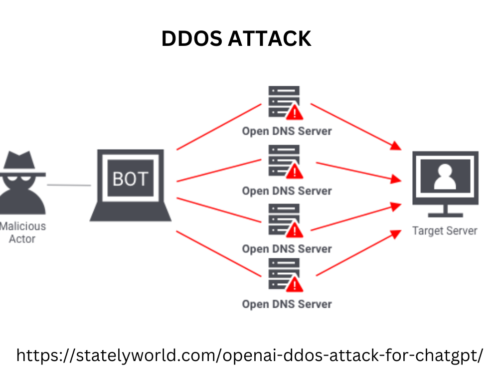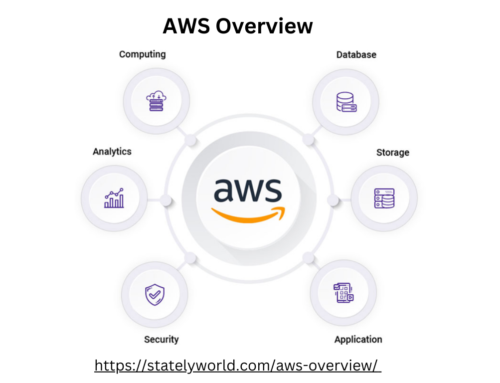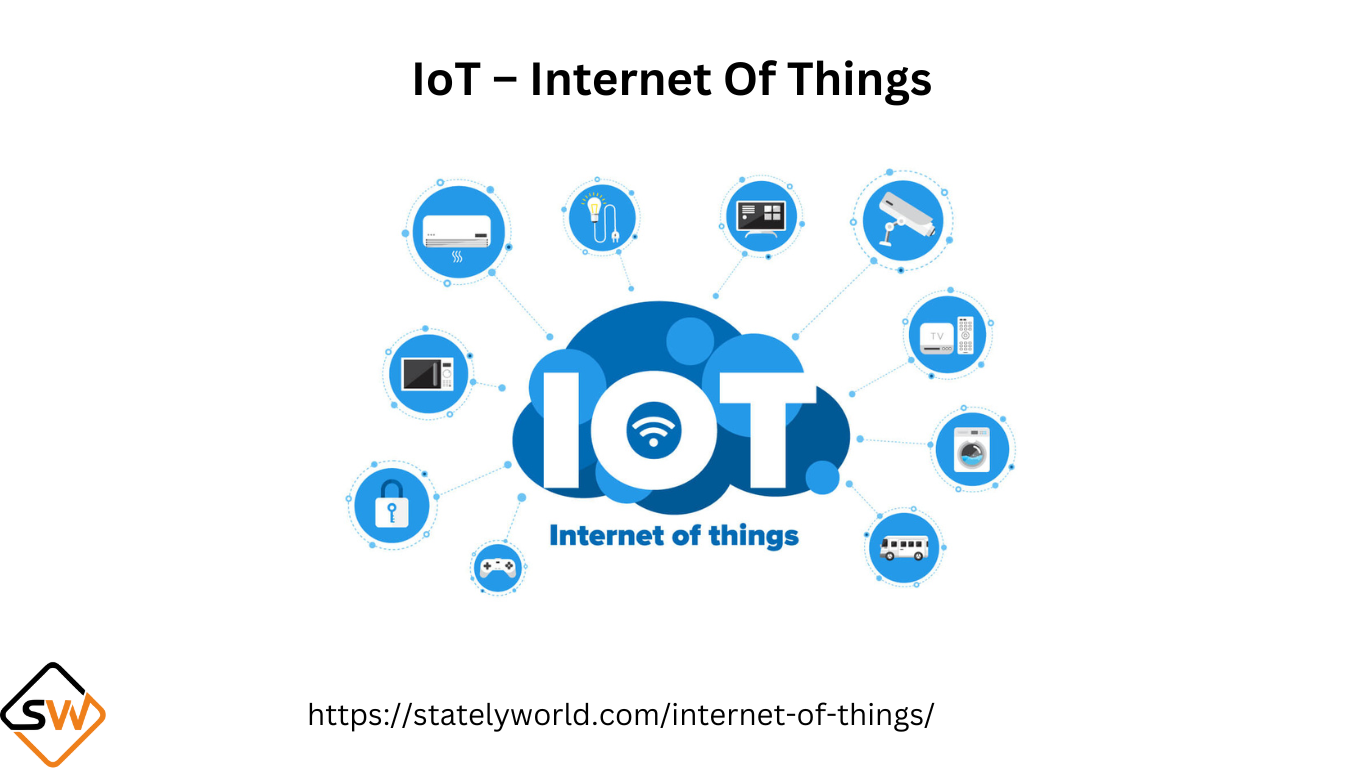
What is the internet of things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is a network of interrelated devices that connect and exchange data with other IoT devices and the cloud. IoT devices are typically embedded with technology such as sensors and software and can include mechanical and digital machines and consumer objects.
OR
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the Internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools.
Increasingly, organizations in a variety of industries are using IoT to operate more efficiently, deliver enhanced customer service, improve decision-making, and increase the value of the business.
With IoT, data is transferable over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interactions.
A thing in the Internet of Things can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, an automobile that has built-in sensors to alert the driver when tire pressure is low, or any other natural or man-made object that can be assigned an Internet Protocol address and is able to transfer data over a network.
What are IoT technologies?
Technologies used in IoT systems may include:
- Edge computing
Edge computing refers to the technology used to make smart devices do more than just send or receive data to their IoT platform. It increases the computing power at the edges of an IoT network, reducing communication latency and improving response time.
- Cloud computing
Cloud technology is used for remote data storage and IoT device management – making the data accessible to multiple devices in the network.
- Machine learning
Machine learning refers to the software and algorithms used to process data and make real-time decisions based on that data. These machine-learning algorithms can be deployed in the cloud or at the edge.
How does IoT work?
A typical IoT system works through the real-time collection and exchange of data. An IoT system has three components:
- Smart devices
This is a device, like a television, security camera, or exercise equipment that has been given computing capabilities. It collects data from its environment, user inputs, or usage patterns and communicates data over the internet to and from its IoT application.
- IoT application
An IoT application is a collection of services and software that integrates data received from various IoT devices. It uses machine learning or artificial intelligence (AI) technology to analyze this data and make informed decisions. These decisions are communicated back to the IoT device and the IoT device then responds intelligently to inputs.
- A graphical user Interface
The IoT device or fleet of devices can be managed through a graphical user interface. Common examples include a mobile application or website that can be used to register and control smart devices.
How does IoT work?
An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems – such as processors, sensors, and communication hardware – to collect, send, and act on data they acquire from their environments.
IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway, which acts as a central hub where IoT devices can send data. Before the data is shared, it can also be sent to an edge device where that data is analyzed locally. Analyzing data locally reduces the volume of data sent to the cloud, which minimizes bandwidth consumption.
Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices – for example, to set them up, give them instructions, or access the data.
The connectivity, networking, and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
Why is IoT important?
IoT helps people live and work smarter. Consumers, for example, can use IoT-embedded devices – such as cars, smartwatches, or thermostats – to improve their lives. For example, when a person arrives home, their car could communicate with the garage to open the door; their thermostat could adjust to a preset temperature; and their lighting could be set to a lower intensity and color.
IoT enables machines to complete tedious tasks without human intervention. Companies can automate processes, reduce labor costs, cut down on waste, and improve service delivery. IoT helps make it less expensive to manufacture and deliver goods and offers transparency into customer transactions.
IoT is one of the most important technologies and it continues to advance as more businesses realize the potential of connected devices to keep them competitive.
What are the pros and cons of IoT?
Some of the advantages of IoT include the following:
- Enables access to information from anywhere at any time on any device.
- Improves communication between connected electronic devices.
- Enables the transfer of data packets over a connected network, which can save time and money.
- Collects large amounts of data from multiple devices, aiding both users and manufacturers.
- Analyzes data at the edge, reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud.
- Automates tasks to improve the quality of a business’s services and reduces the need for human intervention.
- Enables healthcare patients to be cared for continually and more effectively.
Some disadvantages of IoT include the following:
- Increases the attack surface as the number of connected devices grows. As more information is shared between devices, the potential for a hacker to steal confidential information increases.
- This makes device management challenging as the number of IoT devices increases. Organizations might eventually have to deal with a massive number of IoT devices, and collecting and managing the data from all those devices could be challenging.
- Has the potential to corrupt other connected devices if there’s a bug in the system.
- Increases compatibility issues between devices, as there’s no international standard of compatibility for IoT. This makes it difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other.